
|
|
PDF EUA2112QIR1 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | EUA2112QIR1 | |
| Descripción | 25-W Mono Class-D Audio Power Amplifier | |
| Fabricantes | Eutech Microelectronics | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de EUA2112QIR1 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 14 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
EUA2112
25-W Mono Class-D Audio Power
Amplifier with Speaker Protection
DESCRIPTION
The EUA2112 is a high efficiency, one channel
bridged-tied load (BTL), class-D audio power amplifier.
Operating from a 24V power supply, EUA2112 is capable
of delivering 25W of continuous output power to a 8Ω load
with 10% THD+N. The EUA2112 features a differential
input architecture offering improved noise immunity over a
single-ended (SE) input amplifier. Amplifier gain is
internally configured and can be selected to 20, 26, 32 or
36dB utilizing the Go and G1 gain select pins. Advanced
EMI suppression technology enables the use of
inexpensive ferrite bead at the outputs while meeting EMC
requirements.
The speaker protection circuitry is integrated into
EUA2112 to limit the amount of current through the
speaker. The EUA2112 also features short-circuit and
thermal protection preventing the device from being
damaged during a fault condition. The EUA2112 is
available in thermally efficient 28-pin TSSOP package.
FEATURES
z Wide Supply Voltage: 8V to 26V
z Unique Modulation Scheme Reduces EMI Emission
z 25W into an 8-Ω Load From a 24-V Supply
z 20W into a 4-Ω Load From a 12-V Supply
z 94% Efficient Class-D Operation Eliminates
Need for Heat Sinks
z Four Selectable, Gain Settings
z Differential Inputs
z Speaker Protection Circuitry
z Thermal and Short-Circuit Protection
z 28-pin TSSOP Package with Thermal Pad
z RoHS compliant and 100% lead(Pb)-free
Halogen-Free
APPLICATIONS
z Televisions
Typical Application Circuit
DS2112 Ver0.1 Apr. 2010
Figure1. Simplified Application Schematic
1
1 page 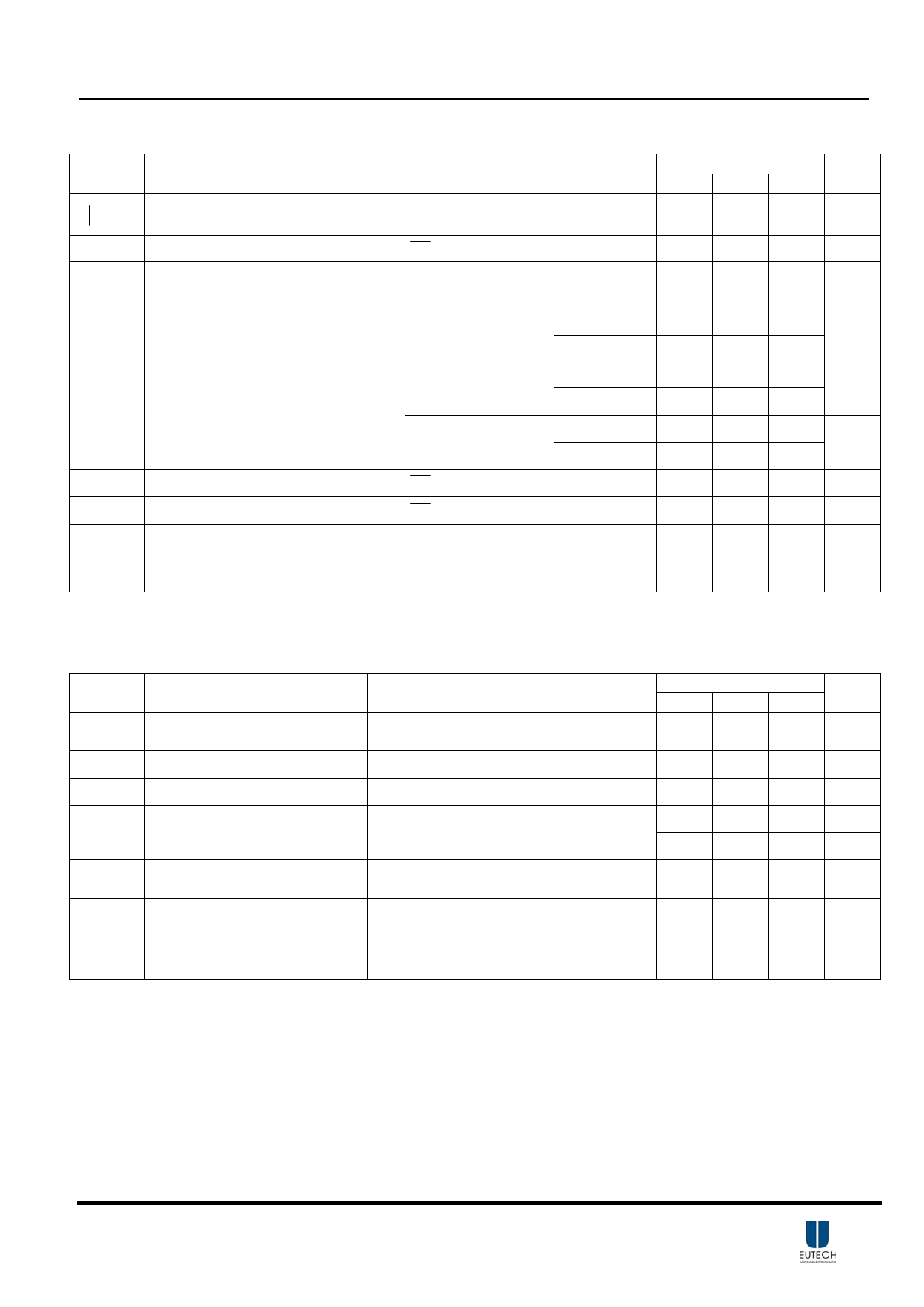
Tel: 0755-8398 3377 / 135 9011 2223 http://www.gofotech.com
EUA2112
DC Characteristics TA = +25°C ,VCC=12V, RL=8Ω (Unless otherwise noted)
Symbol
Parameter
Class-D output offset voltage
VOS (measured differentially)
Conditions
VI= 0V,Gain =36dB
EUA2112
Min Typ Max.
5 50
ICC Quiescent supply current
SD =2V, no load, PVCC=12V
20 35
ICC(SD)
Quiescent supply current in shutdown
mode
SD =0.8V, no load, PVCC=12V
200 1000
rDS(on) Drain-source on-state resistance
VCC=12V,
High Side
IO=500mA, TJ=25°C Low Side
240
240
G Gain
GAIN1=0.8V
GAIN1=2V
GAIN0=0.8V 19 20 21
GAIN0=2V 25 26 27
GAIN0=0.8V 31 32 33
GAIN0=2V 35 36 37
tON Turn-on time
SD =2V
28
tOFF Turn-off time
SD =0.8V
28
GVDD Gate Drive Supply
VO
Output voltage maximum under
PLIMIT control
IGVDD=2mA
V(PLIMIT)=1.3V, VI=1Vrms
4.2 4.5 4.8
6.75 7.90 8.75
Unit
mV
mA
µA
mΩ
dB
dB
ms
ms
V
V
AC Characteristics TA = +25°C ,VCC=24V, RL=8Ω (Unless otherwise noted)
Symbol
Parameter
KSVR Power supply ripple rejection
Conditions
200mVPP ripple at 1kHz,
Gain= 20dB, Inputs ac-coupled to AGND
EUA2112
Min Typ Max.
-60
PO Continuous output power
THD+N=10%, f=1kHz, VCC=24V
25
THD+N Total harmonic distortion +noise VCC=24V, f=1kHz, Po=12.5W( half-power)
0.25
Vn Output integrated noise
20Hz to 22kHz, A-weighted filter,
Gain=20dB
255
-71
SNR Signal-to-noise ratio
PO=12.5W, f=1kHz,Gain=20dB,
A-weighted
91
fOSC Oscillator frequency
230 280 330
Thermal trip point
150
Thermal hysteresis
30
Unit
dB
W
%
µV
dBV
dB
kHz
°C
°C
DS2112 Ver0.1 Apr. 2010
5
5 Page 
Tel: 0755-8398 3377 / 135 9011 2223 http://www.gofotech.com
EUA2112
Gain Selection
The gain of the EUA2112 is set by two input terminals,
GAIN0 and GAIN1.
The gains listed in Table 1 are realized by changing the
taps on the input resistors and feedback resistors inside
the amplifier. This causes the input impedance (ZI) to be
dependent on the gain setting. The actual gain settings are
controlled by ratios of resistors, so the gain variation from
part-to-part is small. However, the input impedance from
part-to-part at the same gain may shift by ±20% due to
shifts in the actual resistance of the input resistors.
For design purposes, the input network should be
designed assuming an input impedance of 40 kΩ, which is
the absolute minimum input impedance of the EUA2112.
At the lower gain settings, the input impedance could
increase as high as 120 kΩ.
POUT
=
R
L
RL
+ 2×
RS
×
VP
2
2×RL
For unclipped power
---------------- (1)
Where:
RS is the total series resistance including RDS(on), and any
resistance in the output filter.
RL is the load resistance.
VP is the peak amplitude of the output possible within
the supply rail.
VP = 6.6 × PLIMIT voltage if PLIMIT < 6.6 × VP
POUT (10%THD) = 1.25 × POUT (unclipped)
Table.2 PLIMIT Typical Operation
Table.1 Gain Setting
AMPLIFIER
INPUT
GAIN1 GAIN0 GAIN (dB) IMPEDANCE (kΩ)
TYP
TYP
00
20
100
01
26
50
10
32
50
11
36
50
SD Operation
Connect SD to a logic high for normal operation. Pulling
SD low causes the outputs to mute and the amplifier to
enter a low-current state. Never leave SD unconnected,
because amplifier operation would be unpredictable.
For the best power-off pop performance, place the
amplifier in the shutdown prior to removing the power
supply voltage.
PLIMIT
The voltage at pin 10 can used to limit the power to levels
below that which is possible based on the supply rail. Add
a resistor divider from GVDD to ground to set the voltage
at the PLIMIT pin. An external reference may also be
used if tighter tolerance is required. Also add a 1µF
capacitor from pin 10 to ground.
The PLIMIT circuit sets a limit on the output
peak-to-peak voltage. The limiting is done by limiting the
duty cycle to fixed maximum value. This limit can be
thought of as a "virtual" voltage rail which is lower than
the supply connected to PVCC. This "virtual" rail is 6
times the voltage at the PLIMIT pin. This output voltage
can be used to calculate the maximum output power for a
given maximum input voltage and speaker impedance.
Test Conditions()
PLIMIT
Voltage
Output Voltage
Output
Amplitude
Power (W)
(VP-P)
PVCC=24V, VIN=1Vrms,
RL=4Ω, Gain=20dB
PVCC=24V, VIN=1Vrms,
RL=4Ω, Gain=20dB
PVCC=24V, VIN=1Vrms,
RL=4Ω, Gain=20dB
PVCC=12V, VIN=1Vrms,
RL=4Ω, Gain=20dB
PVCC=12V, VIN=1Vrms,
RL=4Ω, Gain=20dB
PVCC=12V, VIN=1Vrms,
RL=4Ω, Gain=20dB
4.5
1.24
0.8
4.5
1.13
0.77
25.87
13.48
6.46
18.72
11.7
6.08
28.8
20.7
18.2
24.4
19.3
13.9
GVDD Supply
The GVDD Supply is used to power the gates of the
output full bridge transistors. It can also be used to supply
the PLIMIT voltage divider circuit. Add a 1µF capacitor
to ground at this pin.
DC Detect
EUA2112 has circuitry which will protect the speakers
from DC current which might occur due to defective
capacitors on the input or shorts on the printed circuit
board at the inputs. A DC detect fault will be reported on
the FAULT pin as a low state. The DC Detect fault will
also cause the amplifier to shutdown by changing the state
of the outputs to Hi-Z. To clear the DC Detect it is
necessary to cycle the PVCC supply. Cycling SD will
NOT clear a DC detect fault.
A DC Detect Fault is issued when the output differential
duty-cycle of either channel exceeds 20% (for example,
+60%, -40%) for more than 420 msec at the same polarity.
This feature protects the speaker from large DC currents
or AC currents less than 2Hz. To avoid nuisance faults
due to the DC detect circuit, hold the SD pin low at
DS2112 Ver0.1 Apr. 2010
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 14 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet EUA2112QIR1.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| EUA2112QIR1 | 25-W Mono Class-D Audio Power Amplifier | Eutech Microelectronics |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
