|
|
PDF ICS1892 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | ICS1892 | |
| Descripción | 10Base-T/100Base-TX Integrated PHYceiver | |
| Fabricantes | Integrated Circuit Systems | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de ICS1892 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 30 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc.
ICS1892
Document Type: Data Sheet
Document Stage: Released
10Base-T/100Base-TX Integrated PHYceiver
General
Features
The ICS1892, an enhanced version of the ICS 1890, is a
fully integrated, physical-layer device (PHY) that is
compliant with both the 10Base-T and 100Base-TX
CSMA/CD Ethernet Standard, ISO/IEC 8802-3.
The ICS1892 incorporates digital signal processing (DSP)
in its Physical Medium Dependent (PMD) sublayer. As a
result, it can transmit and receive data on unshielded
twisted-pair (UTP) category 5 cable with attenuation in
excess of 24 dB at 100 MHz. With this ICS-patented
technology, the ICS1892 can virtually eliminate errors from
killer packets.
The ICS1892 supports a broad range of applications: data
terminal equipment (network interface cards and
motherboards), switches, repeaters, bridges, and routers. Its
Media Independent Interface (MII) supports direct
chip-to-chip and motherboard-to-daughterboard
connections as well as connections to an MII connector and
cable. The ICS1892 also provides a Serial Management
Interface for exchanging command and status information
with a Station Management (STA) entity.
The ICS1892 Media Dependent Interface (MDI) can be
configured to provide either half- or full-duplex operation at
data rates of 10 MHz or 100 MHz. The MDI configuration
can be done manually (with input pins or control register
settings) or automatically (using the Auto-Negotiation
features). When the ICS1892 Auto-Negotiation sublayer is
enabled, it exchanges technology capability data with its
remote link partner and automatically selects the
highest-performance operating mode they have in common.
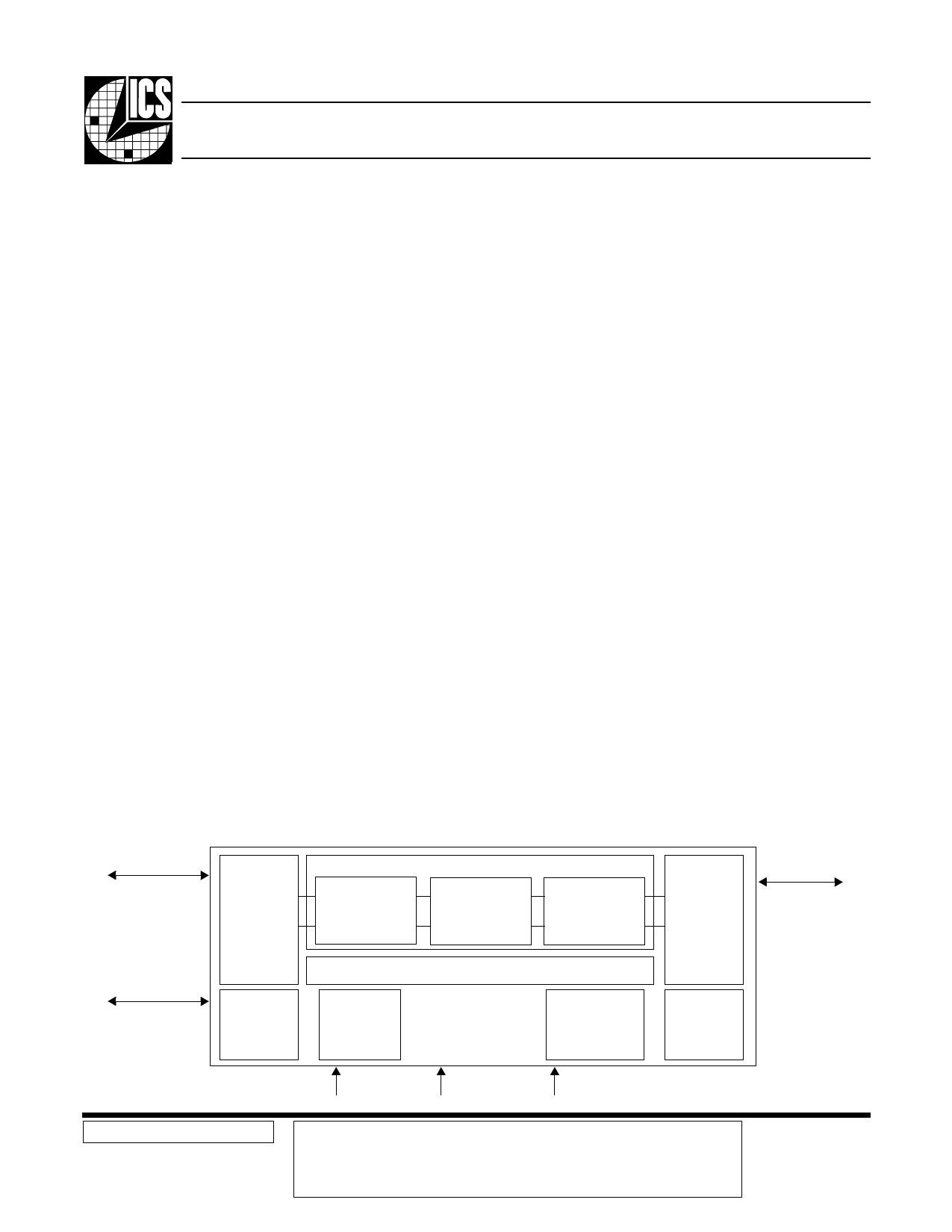
ICS1892 Block Diagram
• Supports category 5 cables with attenuation in excess of
24 dB at 100 MHz across a temperature range from -5° to
+85° C
• DSP-based baseline wander correction to virtually
eliminate killer packets across temperature range of from
-5° to +85° C
• Low-power, 0.5-micron CMOS
• Single 5.0-V power supply.
• Single-chip, fully integrated PHY provides PCS, PMA,
PMD, and AUTONEG sublayers of IEEE standard
• 10Base-T and 100Base-TX IEEE 802.3 compliant
• Fully integrated, DSP-based PMD includes:
– Adaptive equalization and baseline wander correction
– Transmit wave shaping and stream cipher scrambler
– MLT-3 encoder and NRZ/NRZI encoder
• Highly configurable design supports:
– Node, repeater, and switch applications
– Managed and unmanaged applications
– 10M or 100M half- and full-duplex modes
– Parallel detection
– Auto-negotiation, with Next Page capabilities
• MAC/Repeater Interface can be configured as:
– 10M or 100M Media Independent Interface
– 100M Symbol Interface (bypasses the PCS)
– 10M 7-wire Serial Interface
• Provides Loopback Modes for Diagnostic Functions
• Small Footprint 64-pin Low-Profile LQFP and MQFP
packages available
10/100 MII or
Alternate
MAC/Repeater
Interface
MII Serial
Management
Interface
Interface
MUX
MII
Extended
Register
Set
PCS
• Frame
• CRS/COL
Detection
• Parallel to Serial
• 4B/5B
Low-Jitter
Clock
Synthesizer
Clock
100Base-T
PMA
• Clock Recovery
• Link Monitor
• Signal Detection
• Error Detection
10Base-T
TP_PMD
• MLT-3
• Stream Cipher
• Adaptive Equalizer
• Baseline Wander
Correction
Configuration
and Status
Integrated
Switch
Auto-
Negotiation
Twisted-
Pair
Interface to
Magnetics
Modules and
RJ45
Connector
Power
LEDs and PHY
Address
1892 Rev. D, 2/26/01
ICS reserves the right to make changes in the device data identified in
this publication without further notice. ICS advises its customers to
obtain the latest version of all device data to verify that any information
being relied upon by the customer is current and accurate.
1 page 
ICS1892
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Section
8.5
8.5.1
8.5.2
8.5.3
8.6
8.6.1
8.6.2
8.6.3
8.6.4
8.6.5
8.7
8.7.1
8.7.2
8.7.3
8.7.4
8.7.5
8.8
8.8.1
8.8.2
8.8.3
8.8.4
8.8.5
8.8.6
8.9
8.9.1
8.9.2
8.9.3
8.9.4
8.9.5
8.9.6
8.10
8.10.1
8.10.2
8.10.3
8.10.4
8.10.5
Title
Page
Register 3: PHY Identifier Register ............................................................ 73
OUI bits 19-24 (bits 3.15:10) ..................................................................... 73
Manufacturer's Model Number (bits 3.9:4) ................................................ 73
Revision Number (bits 3.3:0) ..................................................................... 74
Register 4: Auto-Negotiation Register ....................................................... 75
Next Page (bit 4.15) ................................................................................... 75
IEEE Reserved Bit (bit 4.14) ...................................................................... 76
Remote Fault (bit 4.13) .............................................................................. 76
Technology Ability Field (bits 4.12:5) ......................................................... 76
Selector Field (Bits 4.4:0) .......................................................................... 77
Register 5: Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register ........................ 78
Next Page (bit 5.15) ................................................................................... 78
Acknowledge (bit 5.14) .............................................................................. 79
Remote Fault (bit 5.13) .............................................................................. 79
Technology Ability Field (bits 5.12:5) ......................................................... 79
Selector Field (bits 5.4:0) ........................................................................... 79
Register 6: Auto-Negotiation Expansion Register ..................................... 80
IEEE Reserved Bits (bits 6.15:5) ............................................................... 80
Parallel Detection Fault (bit 6.4) ................................................................ 81
Link Partner Next Page Able (bit 6.3) ........................................................ 81
Next Page Able (bit 6.2) ............................................................................ 81
Page Received (bit 6.1) ............................................................................. 81
Link Partner Auto-Negotiation Able (bit 6.0) .............................................. 81
Register 7: Auto-Negotiation Next Page Transmit Register ...................... 82
Next Page (bit 7.15) ................................................................................... 83
IEEE Reserved Bit (bit 7.14) ...................................................................... 83
Message Page (bit 7.13) ........................................................................... 83
Acknowledge 2 (bit 7.12) ........................................................................... 83
Toggle (bit 7.11) ........................................................................................ 83
Message Code Field / Unformatted Code Field (bits 7.10:0) .................... 83
Register 8: Auto-Negotiation Next Page Link Partner Ability Register ...... 84
Next Page (bit 8.15) ................................................................................... 85
IEEE Reserved Bit (bit 8.14) ...................................................................... 85
Message Page (bit 8.13) ........................................................................... 85
Acknowledge 2 (bit 8.12) ........................................................................... 85
Message Code Field / Unformatted Code Field (bits 8.10:0) .................... 85
ICS1892, Rev. D, 2/26/01
© 2000-2001, Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
5
February 26, 2001
5 Page 
ICS1892
Chapter 2 Conventions and Nomenclature
Chapter 2 Conventions and Nomenclature
Table 2-1 lists and explains the conventions and nomenclature used throughout this data sheet.
Table 2-1. Conventions and Nomenclature
Item
Asterisk (*)
Bits
Code groups
Colon (:)
Numbers
Pin (or signal) names
Convention / Nomenclature
Within this table, see the item ‘Pin (or signal) names’
• A bit in a register is identified using the format ‘register.bit’. For example, bit
0.15 is bit 15 of register 0.
• When a colon is used with bits, it indicates the range of bits. For example,
bits 1.15:11 are bits 15, 14, 13, 12, and 11 of register 1.
• For a range of bits, the order is always from the most-significant bit to the
least-significant bit.
Within this table, see the item ‘Symbols’
Within this table, see these items:
• ‘Bits’
• ‘Pin (or signal) names’
• As a default, all numbers use the decimal system (that is, base 10) unless
followed by a lowercase letter. A string of numbers followed by a lowercase
letter:
– A ‘b’ represents a binary (base 2) number
– An ‘h’ represents a hexadecimal (base 16) number
– An ‘o’ represents an octal (base 8) number
• All numerical references to registers use decimal notation (and not
hexadecimal).
• All pin or signal names are provided in capital letters.
• A pin name that includes a forward slash ‘/’ is a multi-function, configuration
pin. These pins provide the ability to select between two ICS1892
functions. The name provided:
– Before the ‘/’ indicates the pin name and function when the signal level
on the pin is logic zero.
– After the ‘/’ indicates the pin name and function when the signal level on
the pin is logic one.
For example, the HW/SW pin selects between Hardware (HW) mode and
Software (SW) mode.
– When the signal level on the HW/SW pin is logic zero, the ICS1892
Hardware mode is selected.
– When the signal level on the HW/SW pin is logic one, the ICS1892
Software mode is selected.
• An asterisk appended to the end of a pin name or signal name (such as
RESET*) indicates an active-low operation.
• When a colon is used with pin or signal names, it indicates a range. For
example, TXD[3:0] represents pins/signals TXD3, TXD2, TXD1, and TXD0.
• When pin name abbreviations are spelled out, words in parentheses
indicate additional description that is not part of the pin name abbreviation.
ICS1892, Rev. D, 2/26/01
© 2000-2001, Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
11
February 26, 2001
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 30 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet ICS1892.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| ICS1890 | 10Base-T/100Base-TX Integrated PHYceiver | Integrated Circuit Systems |
| ICS1892 | 10Base-T/100Base-TX Integrated PHYceiver | Integrated Circuit Systems |
| ICS1893 | 3.3-V 10Base-T/100Base-TX Integrated PHYceiver | Integrated Circuit Systems |
| ICS1893AF | 3.3V 10Base-T/100Base-TX Integrated PHYceiverTM | Integrated Circuit Systems |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |