
|
|
PDF DDC112 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | DDC112 | |
| Descripción | Dual Current Input 20-Bit ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER | |
| Fabricantes | Burr-Brown Corporation | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de DDC112 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 24 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
®
For most current data sheet and other product
information, visit www.burr-brown.com
DDC112
DDC112
Dual Current Input 20-Bit
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
FEATURES
q MONOLITHIC CHARGE MEASUREMENT ADC
q DIGITAL FILTER NOISE REDUCTION:
3.2ppm, rms
q INTEGRAL LINEARITY:
±0.005% Reading ±0.5ppm FSR
q HIGH PRECISION, TRUE INTEGRATING
FUNCTION
q PROGRAMMABLE FULL SCALE
q SINGLE SUPPLY
q CASCADABLE OUTPUT
APPLICATIONS
q DIRECT PHOTOSENSOR DIGITIZATION
q CT SCANNER DAS
q INFRARED PYROMETER
q PRECISION PROCESS CONTROL
q LIQUID/GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
q BLOOD ANALYSIS
Protected by US Patent #5841310
DESCRIPTION
The DDC112 is a dual input, wide dynamic range,
charge-digitizing analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with
20-bit resolution. Low level current output devices,
such as photosensors, can be directly connected to its
inputs. Charge integration is continuous as each input
uses two integrators; while one is being digitized, the
other is integrating.
For each of its two inputs, the DDC112 combines
current-to-voltage conversion, continuous integration,
programmable full-scale range, A/D conversion, and
digital filtering to achieve a precision, wide dynamic
range digital result. In addition to the internal program-
mable full-scale ranges, external integrating capacitors
allow an additional user-settable full-scale range of up
to 1000pC.
To provide single-supply operation, the internal ADC
utilizes a differential input, with the positive input tied
to VREF. When the integration capacitor is reset at the
beginning of each integration cycle, the capacitor
charges to VREF. This charge is removed in proportion
to the input current. At the end of the integration cycle,
the remaining voltage is compared to VREF.
The high-speed serial shift register which holds the
result of the last conversion can be configured to allow
multiple DDC112 units to be cascaded, minimizing
interconnections. The DDC112 is available in a SO-28
package and is offered in two performance grades.
CAP1A
CAP1A
IN1
CAP1B
CAP1B
CAP2A
CAP2A
IN2
CAP2B
CAP2B
AVDD AGND
CHANNEL 1
Dual
Switched
Integrator
CHANNEL 2
Dual
Switched
Integrator
VREF
DVDD DGND
∆Σ
Modulator
DCLK
Digital
Filter
Digital
Input/Output
DVALID
DXMIT
DOUT
DIN
Control
RANGE2
RANGE1
RANGE0
TEST CONV CLK
International Airport Industrial Park • Mailing Address: PO Box 11400, Tucson, AZ 85734 • Street Address: 6730 S. Tucson Blvd., Tucson, AZ 85706 • Tel: (520) 746-1111
Twx: 910-952-1111 • Internet: http://www.burr-brown.com/ • Cable: BBRCORP • Telex: 066-6491 • FAX: (520) 889-1510 • Immediate Product Info: (800) 548-6132
©1997 Burr-Brown Corporation
PDS-14121D
DDC112Printed in U.S.A. January, 2000
®
1 page 
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES (Cont.)
At TA = +25°C, characterization done with Range 5 (250pC), TINT = 500µs, VREF = +4.096, AVDD = DVDD = +5V, and CLK = 10MHz, unless otherwise noted.
OFFSET DRIFT vs TEMPERATURE
100
All Ranges
50
0
–50
–100
25
35
45 55 65
Temperature (°C)
75 85
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
1
INPUT VOS vs RANGE
2 34 56
Range
7
ANALOG SUPPLY CURRENT vs TEMPERATURE
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
–40 –15
10
35
60
Temperature (°C)
85
DIGITAL SUPPLY CURRENT vs TEMPERATURE
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–40 –15
10
35
60
Temperature (°C)
85
CROSSTALK vs FREQUENCY
0
–20
Separation Measured
–40 Between Inputs 1 and 2
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
0
100 200 300 400
Frequency (Hz)
500
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO vs FREQUENCY
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
0 25 50 75 100
Frequency (KHz)
®
5 DDC112
5 Page 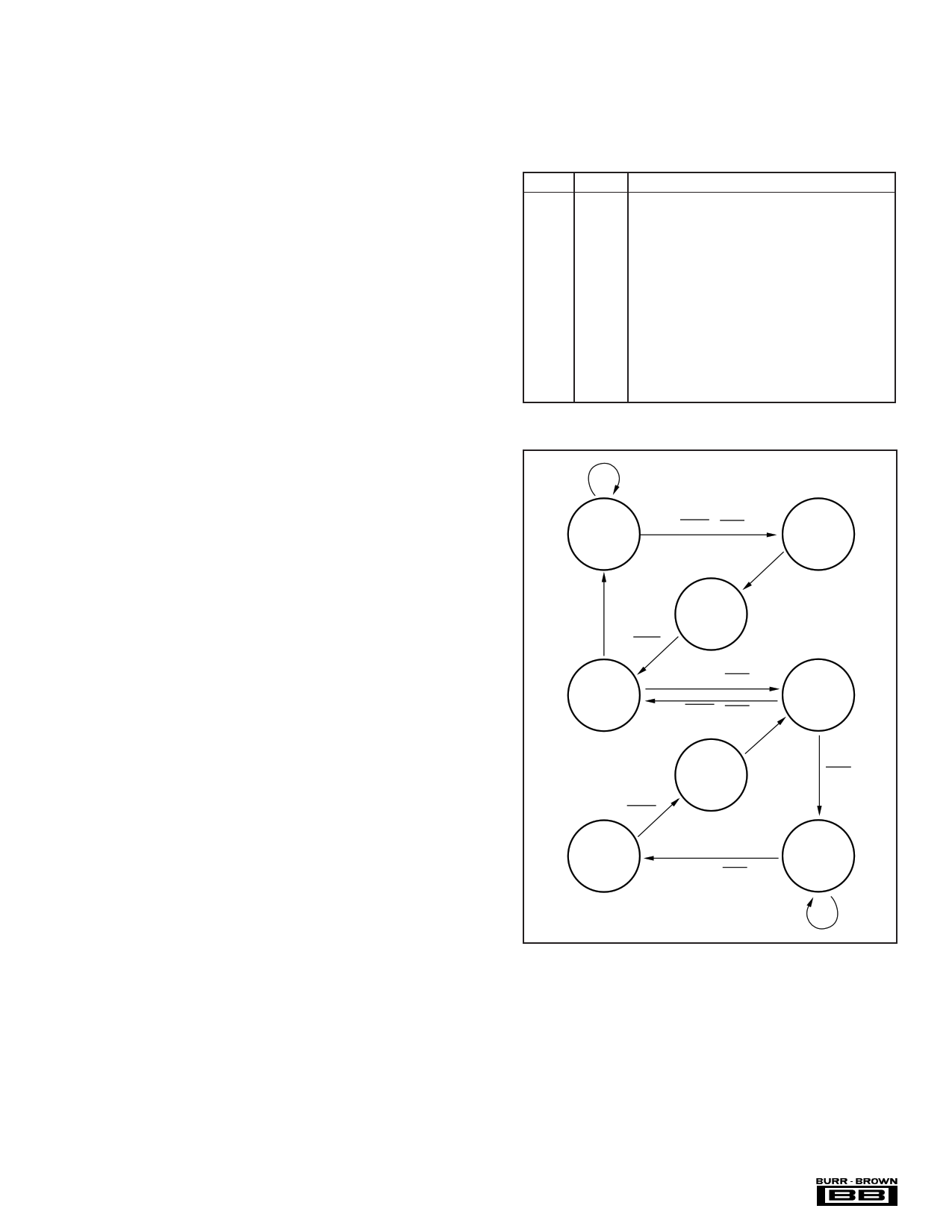
TEST and CONV work together to implement this feature.
The test mode is entered when TEST is HIGH prior to a
CONV edge. At that point, a CONV edge triggers the
grounding of the analog inputs and the switching of 13pC
packets of charge onto the integration capacitors. If TEST is
kept HIGH through at least two conversions (i.e., a rise and
fall of CONV), all four integrators will be charged with a
13pC packet. At the end of each conversion, the voltage at
the output of the integrators is digitized as discussed in the
“Continuous Mode” and “Non-Continuous Mode” section
of this data sheet. The test mode is exited when TEST is
LOW and a CONV edge occurs.
Once the test mode is entered as described above, TEST can
cycle as many times as desired. When this is done, additional
13pC packets are added on the rising edge of TEST to the
existing charge on the integrator capacitors. Multiple charge
packets can be added in this way as long as the TEST pin is
not LOW when CONV toggles.
DIGITAL ISSUES
The digital interface of the DDC112 provides the digital
results via a synchronous serial interface consisting of a data
clock (DCLK), a transmit enable pin (DXMIT), a valid data
pin (DVALID), a serial data output pin (DOUT), and a serial
data input pin (DIN). The DDC112 contains only one A/D
converter, so the conversion process is interleaved between
the two inputs (see Figure 2). The integration and conversion
process is fundamentally independent of the data retrieval
process. Consequently, the CLK frequency and DCLK fre-
quencies need not be the same. DIN is used when multiple
converters are cascaded. Cascading or “daisy chaining”
greatly simplifies the interconnection and routing of the
digital outputs in cases where a large number of converters
are needed. Refer to “Cascading Multiple Converters” section
of this data sheet for more detail.
The conversion rate of the DDC112 is set by a combination
of the integration time (determined by the user) and the speed
of the A/D conversion process. The A/D conversion time is
primarily a function of the system clock (CLK) speed. One
A/D conversion cycle encompasses the conversion of two
signals (one from each input of the DDC112) and reset time
for each of the integrators involved in the two conversions. In
most situations, the A/D conversion time is shorter than the
integration time. If this condition exists, the DDC112 will
operate in the continuous mode. When the DDC112 is in the
continuous mode, the sensor output is continuously integrated
by one of the two sides of each input.
In the event that the A/D conversion takes longer than the
integration time, the DDC112 will switch into a non-con-
tinuous mode. In non-continuous mode, the A/D converter is
not able to keep pace with the speed of the integration
process. Consequently, the integration process is periodi-
cally halted until the digitizing process catches up. These
two basic modes of operation for the DDC112—continuous
and non-continuous modes—are described below.
Continuous and Non-Continuous
Operational Modes
The state diagram of the DDC112 is shown in Figure 9. In
all, there are 8 states. Table IV provides a brief explanation
of each of the states.
STATE
1
MODE
Ncont
2 Ncont
3 Cont
4 Cont
5 Cont
6 Cont
7 Ncont
8 Ncont
DESCRIPTION
Complete m/r/az of side A, then side B (if previous
state is state 4). Initial power-up state when CONV
is initially held HIGH.
Prepare side A for integration.
Integrate on side A.
Integrate on side B; m/r/az on side A.
Integrate on side A; m/r/az on side B.
Integrate on side B.
Prepare side B for integration.
Complete m/r/az of side B, then side A (if previous
state is state 5). Initial power-up state when CONV
is initially held LOW.
TABLE IV. State Descriptions.
mbsy
1
Ncont
CONV • mbsy
2
Ncont
CONV • mbsy
CONV
4
Int B/Meas A
Cont
3
Int A
Cont
CONV
CONV • mbsy
CONV • mbsy
5
Int A/Meas B
Cont
CONV
7
Ncont
6
Int B
Cont
CONV
CONV • mbsy
CONV • mbsy
8
Ncont
mbsy
FIGURE 9. State Diagram.
Four signals are used to control progression around the state
diagram: CONV and mbsy and their complements. The state
machine uses the level as opposed to the edges of CONV to
control the progression. mbsy is an internally generated
signal not available to the user. It is active whenever a
measurement/reset/auto-zero (m/r/az) cycle is in progress.
®
11 DDC112
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 24 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet DDC112.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| DDC112 | Dual Current Input 20-Bit ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER | Burr-Brown Corporation |
| DDC112 | Precision/ High-Speed Transimpedance Amplifier | Burr-Brown Corporation |
| DDC112 | DDC112: Dual Current Input 20-Bit Analog-To-Digital Converter (Rev. B) | Texas Instruments |
| DDC1128 | DDC1128 128-Channel Current-Input Analog-to-Digital Converter | Texas Instruments |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
